The latest upgrade adds escrow swaps — a fundamentally new execution layer — to Omniston’s liquidity aggregation engine. Escrow swaps are already live and powering xStocks swaps on STON.fi, enabling direct Asset-1 → Asset-2 execution alongside traditional DEX routing. Below, we break down how escrow swaps work, why they matter, and how they fit into the long-term evolution of Omniston.
| In #STONchronicles we share the technical breakthroughs and product milestones that showcase our commitment to building the future of DeFi on TON. |
Escrow swaps move Omniston closer to the architecture we’re building: an execution engine where different liquidity models — DEX pools, resolver-driven OTC quotes, specialized contracts, and future mechanisms on TON — compete on equal footing. Users see a single swap interface; underneath it, the protocol evaluates fundamentally different execution paths and selects the best outcome.
Why this matters
With escrow swaps now integrated into Omniston, we’ve introduced an execution model that didn’t previously exist on TON: resolver-driven, escrow-based swaps that can access private OTC liquidity alongside public DEX pools.
Until now, Omniston unified liquidity coming from connected DEX pools. These pools provide depth and multi-step routing, but they rely on public AMM liquidity and operate through chains of intermediate assets.
Escrow contracts introduce a fundamentally different execution mechanism: direct Asset-1 → Asset-2 swaps using resolver-driven pricing. This allows Omniston to tap into private OTC liquidity, which may outperform AMM pool routes depending on market conditions.
💡 xStocks — tokenized assets issued by Backed Finance — are the first to use escrow execution inside Omniston. Instead of relying on public pool liquidity, xStocks swaps tap into private OTC liquidity through escrow contracts that match users with competitive resolvers. Each xStock is backed 1:1 by real-world assets, behaves like a TON jetton in a wallet, and now benefits from institutional-grade execution with full on-chain transparency.
What we’ve built
We’ve developed the escrow swap contract and integrated it into Omniston. The protocol treats escrow swaps as a native execution layer alongside DEX routes, with settlement enforced fully on-chain by escrow smart contracts.
Users do not choose routes manually. Omniston automatically selects the most cost-efficient mechanism based on price and execution conditions — not on the type of liquidity source.
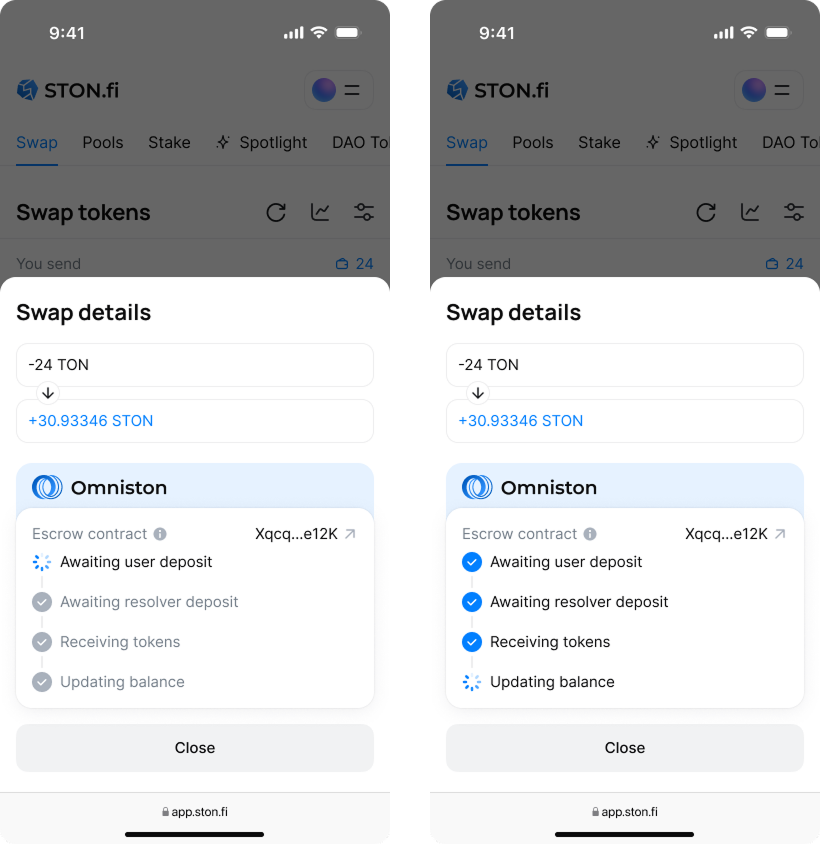
Fully decentralized and safe
Escrow swaps maintain STON.fi’s core principle of full decentralization. Every transaction is executed through on-chain smart contracts with atomic settlement: either the swap completes in full, or nothing happens. Resolvers provide pricing but never custody user funds or control execution, ensuring institutional-grade execution without sacrificing user ownership or transparency.
What this gives users
For users, this means deeper liquidity access, better pricing through OTC competition, and simpler execution. Direct token-to-token swaps eliminate unnecessary intermediates, while trustless escrow settlement adds an additional layer of safety.
The direct Asset-1-to-Asset-2 exchange also eliminates scenarios where a multi-hop route might leave a user holding an intermediate asset.
The user experience remains simple — “Swap”, but under the hood Omniston becomes a stronger aggregator, comparing fundamentally different execution models and choosing the optimal one.
Where this leads the protocol
Escrow swaps are part of a broader strategy: turning Omniston into an execution engine where multiple liquidity and execution models — AMMs, OTC resolvers, and future mechanisms — compete on equal footing, and the protocol consistently selects the best possible outcome.
As TON grows, more liquidity sources and contract types will appear. Omniston becomes the place where they converge. Adding the escrow layer is the first step in that direction.
| Read also: xStocks: explore tokenized market |